Section: New Results
Markov Random Fields
New hierarchical joint classification method of SAR and optical multiresolution remote sensing datas
Participants : Ihsen Hedhli, Josiane Zerubia [contact] .
This work was carried out in collaboration with Prof. Gabriele Moser and Prof. Sebastiano Serpico from DITEN departement [www.diten.unige.it/ ], University of Genoa, Italy.
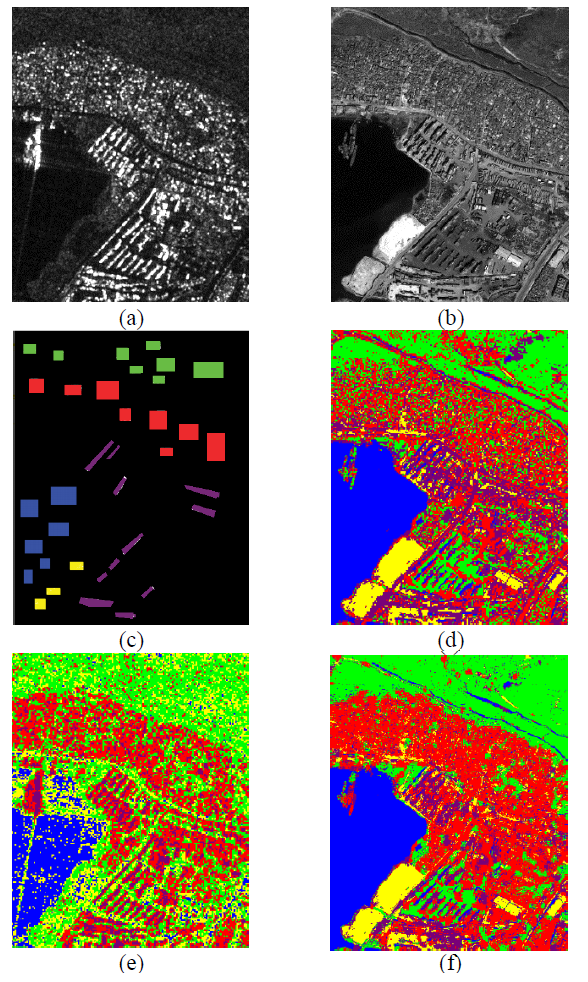
Nowadays, a wide variety of remote sensing images is available. Therefore, it becomes more and more important to be able to analyze compound data sets consisting of different types of images acquired by different sensors, as they allow a spatially distributed and temporally repetitive view of the monitored area at the desired spatial scales. In particular, the opportunity of joint availability of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and optical images offers high resolution (HR), all-weather, day/night, short revisit time data, as well as polarimetric and multifrequency acquisition capabilities. Similarly, the strong differences in terms of wavelength range (microwave vs. visible and near infrared), sensitivity to cloud cover and sun illumination (strong for optical imagery vs. almost negligible for SAR), and noise-like properties (speckle in SAR vs. generally low noise variance in current HR optical sensors) make the joint use of HR optical and SAR imagery especially interesting for many applications to environmental monitoring and natural risk management. Within this framework, there is a definite need for classification methods that automatically correlate different sets of images taken on the same area from different sensors and at different resolutions. This year we developed a novel classification approach for multiresolution, multisensor (optical and synthetic aperture radar), and/or multiband images. Accurate and time-efficient classification methods are particularly important tools to support rapid and reliable assessment of the ground changes. Given the huge amount and variety of data available currently from last-generation satellite missions, the main difficulty is to develop a classifier that can benefit from multiband, multiresolution, and multisensor input imagery. As shown in Figure 1 , the proposed method addresses the problem of multisensor fusion of SAR with optical data for classification purposes, and allows input data collected at multiple resolutions and additional multiscale features derived through wavelets to be fused. The proposed approach formalizes a supervised Bayesian classifier within a multiple quadtree topology that combines a class-conditional statistical model for pixel-wise information and a hierarchical Markov random field (MRF) for multisensor and multiresolution contextual information.
|